
Guide to 3D Printing Miniatures: Ensuring Precision in Your Models

(Credit: Jakub Zerdzicki)
3D printing is a technology that has only evolved more and more since its creation, leading to an entire industry behind it. While 3D printing different kinds of products have diverse applications, none other seems to grab the attention of the general populace than miniature printing.
Whether they serve as game elements in TTRPGS, board games, props in movie sets, or architectural models, miniatures are a well-sought-after item in several communities.
With 3D printers now more accessible to the average person, more and more people are 3D printing miniatures themselves. However, there are several things that one must consider before making their tiny-sized figurines, such as the appropriate materials and software.
This article aims to put all these queries to rest, serving as a complete guide to teaching you how to 3D print miniatures.
Types of 3D Printing Technologies for Miniatures:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, encompasses several technologies. Each of them has its strengths and applications, from rapid prototyping to the production of final products, across industries including automotive, aerospace, medical, consumer products, and more.
Here are the primary types of 3D printing technologies.
1. Stereolithography (SLA)
One of the earliest 3D printing techniques uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization. It’s known for producing parts with high detail and smooth surfaces.
2. Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Similar to SLA, DLP uses a digital light projector to flash a single image of each layer all at once. It tends to be faster than SLA because the entire layer is cured simultaneously.
3. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) / Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
This technology extrudes thermoplastic materials layer by layer from a filament spool through a heated nozzle to build an object. It’s the most widely used 3D printing technology due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of use.
4. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Uses a laser to sinter powdered material, typically nylon or polyamide, binding it together to create a solid structure. It does not require support structures since the powder acts as a self-supporting material, allowing for complex geometries.
5. Selective Laser Melting (SLM) & Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
These technologies are similar to SLS but specifically designed for metal powders. They fully melt the powder, creating strong and dense structures. SLM and DMLS are widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
6. Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
Developed by HP, it uses a detailing agent applied around the edges of each layer to precisely define part details. Infrared energy then fuses the entire layer. MJF is known for its speed and ability to produce parts with consistent mechanical properties.
Design and Modeling Software for 3D Printing Miniatures
Designing and modeling 3D miniatures for printing requires software that can provide detailed sculpting capabilities, efficient modeling tools, and compatibility with 3D printing technologies. Here are some popular software options that cater to different aspects of 3D miniature design, from the initial concept to the final model ready for printing:
1. Blender
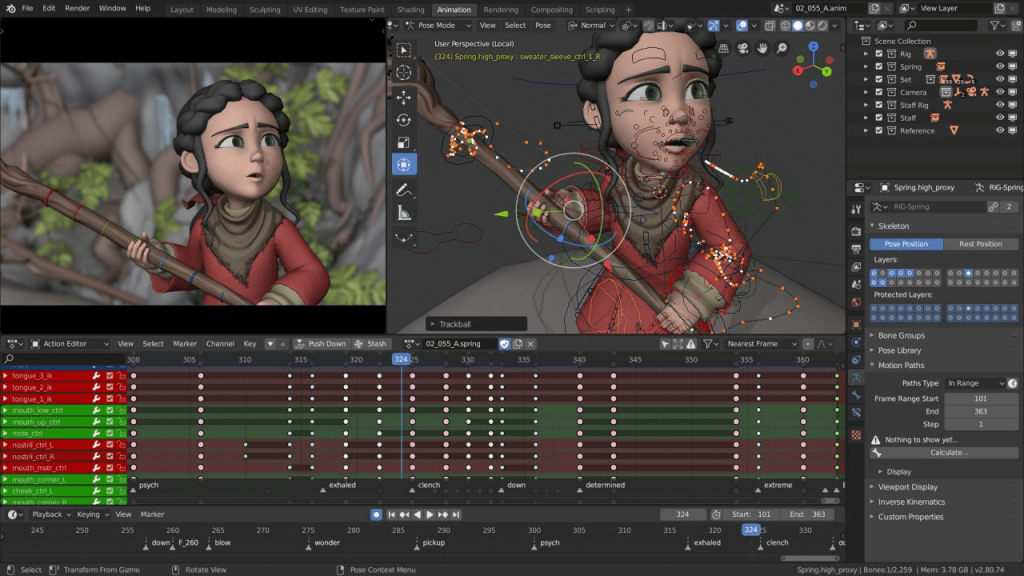
Blender gives the option to experiment with all types of 3D design in one simple program (Credit: Blender)
Blender is an open-source 3D creation suite that supports the entirety of the 3D pipeline—modeling, rigging, animation, simulation, rendering, compositing, and motion tracking, even video editing, and game creation. It’s well-known for its powerful features and zero cost. Blender is used by hobbyists and professionals alike in various industries, including film, animation, video games, and design.
2. ZBrush
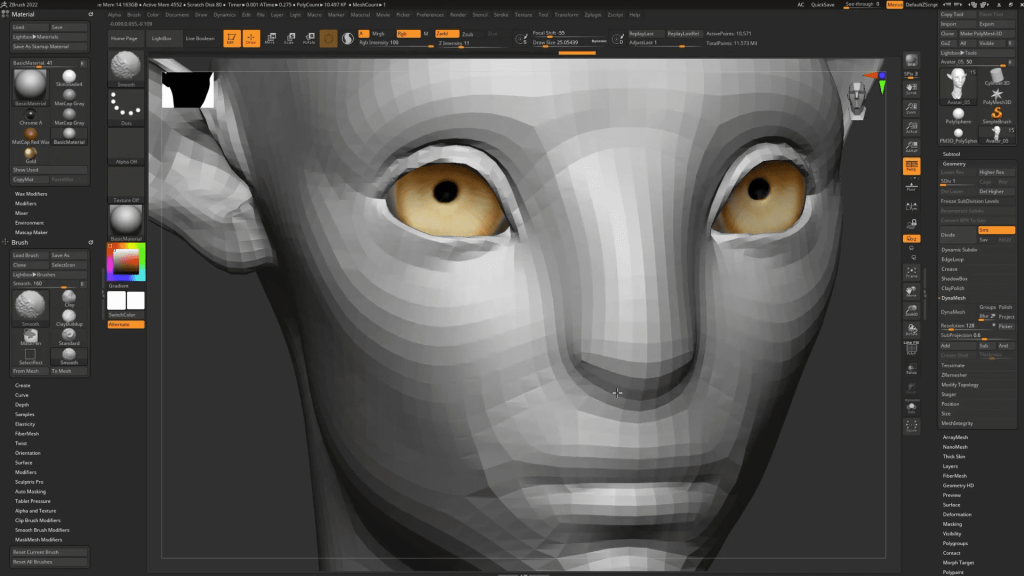
Sculpt your miniature models with ZBrush’s innovative technology (Credit: ZBrush)
ZBrush is a digital sculpting tool that combines 3D/2.5D modeling, texturing, and painting. It uses a proprietary pixel technology that stores lighting, color, material, orientation, and depth information for the points making up all objects on the screen. ZBrush is particularly renowned for its ability to create highly detailed models, making it a favorite in the film, game development, and multimedia industries.
3. Tinkercad
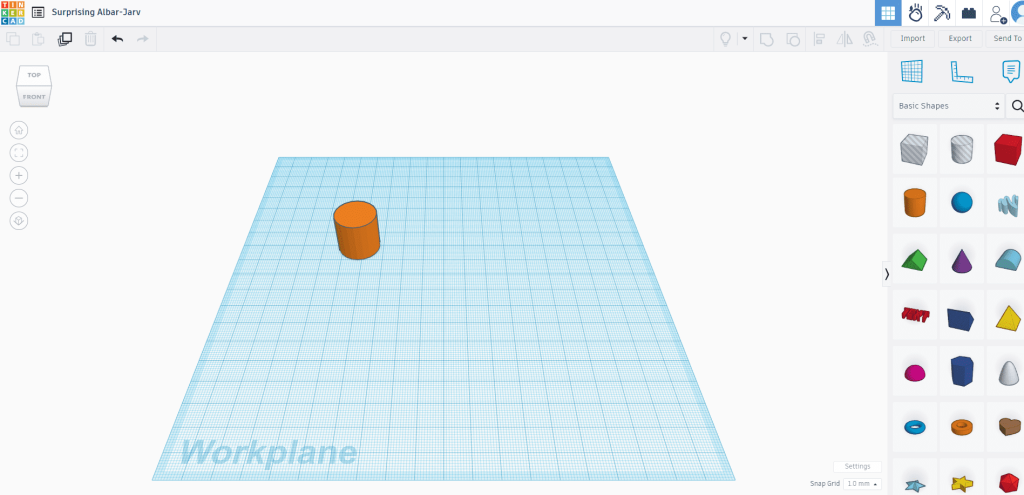
Tinkercad is an easy software for beginners to experiment with 3D modeling (Credit: Tinkercad)
Tinkercad is a free, online 3D modeling program that runs in a web browser and is known for its simplicity and ease of use. It’s aimed at beginners, educators, and hobbyists interested in 3D design, electronics, and coding, making it a popular choice for introductory 3D printing and design projects, especially in schools.
4. Fusion 360

Fusion350 allows 3D modeling elements that can design miniatures for all different purposes (Credit: Cadline)
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based CAD, CAM, CAE, and PCB software platform for product design and manufacturing. Designed by Autodesk, it offers an integrated set of tools for 3D design, simulation, and manufacturing processes. Fusion 360 is aimed at students, hobbyists, and professionals in the design, mechanical engineering, and manufacturing industries.
5. SOLIDWORKS
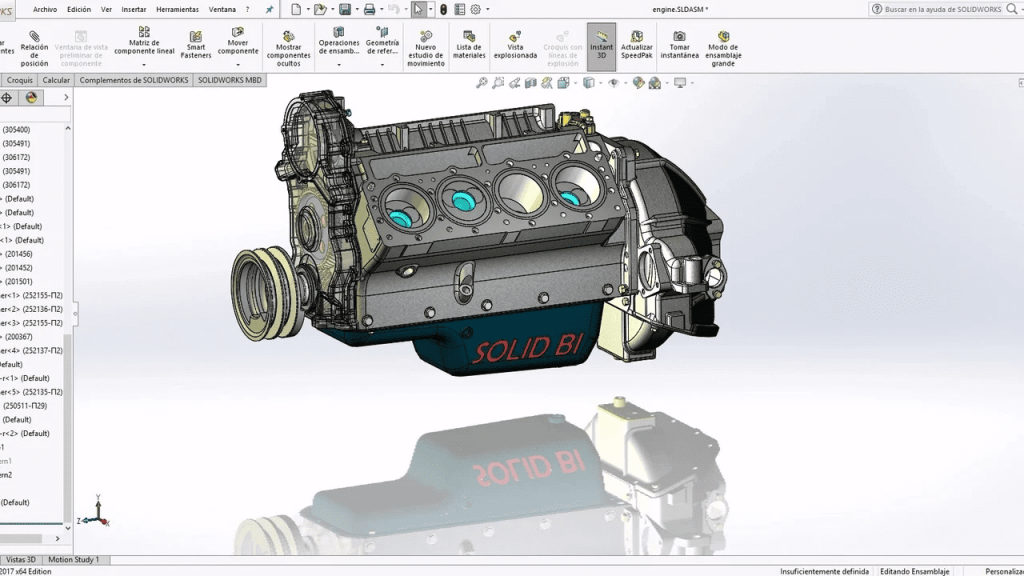
SOLIDWORKS is a practical software that aims to model the most industrial of miniatures (Credit: All3DP)
SOLIDWORKS is a solid modeling computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE) computer program that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. Developed by Dassault Systèmes, it’s widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and product design for creating parts, assemblies, and detailed drawings.
3D Printing Materials for Miniatures: A Comparative Analysis
So in this section, below mentioned are some of the most popular materials for 3D-printed miniatures. There are a total of 4 materials listed out, and they are:
PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is well-known for being user-friendly and environmentally friendly, making it a great option for novices. It can be printed at lower temperatures, has a large color gamut, and gives good detail. It is more brittle and less resilient than other materials, though.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS, is a strong and long-lasting material that works well for functional parts that need to be robust. Although it can tolerate greater temperatures, when printing it releases fumes and needs a heated bed to keep from warping.
Resin: Excellent detail and silky finishes make it ideal for detailed miniatures. It needs UV post-processing and a particular kind of printer (SLA/DLP). Compared to materials based on filaments, resin prints are more costly and fragile.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Combines the strength and durability more akin to ABS with the printing simplicity of PLA. Although it can be prone to stringing and needs careful temperature management, it is resistant to chemicals and dampness.
Comparison of Different 3D Printing Materials
When venturing into the world of 3D printing miniatures, choosing the right material is pivotal. Below, we break down the characteristics, best uses, pros, and cons of four widely used materials: PLA, ABS, Resin, and PETG.
|
Material |
Characteristics |
Best Uses |
Pros |
Cons |
|
PLA (Polylactic Acid) |
Biodegradable, made from renewable resources, sweet smell when printed |
Detailed models, decorative items, and prototypes not subjected to high heat |
Easy to print, wide color variety, no heated bed required |
Less durable, compared to some other 3D printing materials, not heat-resistant |
|
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) |
Petroleum-based, tough, impact-resistant |
Functional parts, heat-resistant applications |
Durable, can be acetone smoothed, good for mechanical parts |
Emits fumes and requires a heated bed, which can be challenging to print with. |
|
Resin |
Liquid polymer hardens under UV light, has high detail, and smooth finishes |
Miniatures with intricate details, jewelry, medical models |
High detail resolution, smooth finish, strong when cured |
Requires post-processing, expensive, brittleness |
|
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) |
Glycol-modified PET, flexible and strong |
Durable and flexible functional prints |
Impact-resistant, moisture and chemical-resistant, durable |
Pronte to stringing and blobbing, and does require fine-tuning of settings. |
Each material has its own set of benefits and challenges, and the best choice depends on the specific requirements of your project, including the desired level of detail, durability, and your experience level with 3D printing. To know more information similar to this, check out the comparison guide between PETG and PLA.
Choosing the Best Material for Your 3D Miniatures:
Choosing the right material for your 3D printing project involves assessing the specific requirements of your design and how you intend to use the finished product. Here’s a streamlined approach:
1. Defining the Purpose of Your Print
Ascertain whether the print is intended for ornamental usage, utilitarian use, or exposure to external influences and stress. While utilitarian pieces may need the strength and durability of ABS or PETG, decorative items can benefit from the delicate details of Resin.
2. Assessing Detail Requirements
Think about how much detail your miniature requires. Unlike PLA or ABS, which might not represent the smallest features as precisely, the resin may be ideal if your project has fine elements because of its greater detail resolution. PLA or PETG could be enough for larger, less complex products.
3. Ensuring Durability
Consider how much you want your miniature to be able to endure elements such as aging, stress from external impact, and temperature changes. Use ABS or PETG for things that must endure heat, mechanical stress, or outdoor environments. When compared to PLA, these materials offer greater resilience to environmental conditions and durability.
4. Compatibility with Your Printer
A big part is your level of experience and the features of your 3D printer. Verify the printer’s specifications to make sure the material you select is compatible with it. While most FDM printers can handle PLA, ABS, and PETG with variable degrees of ease, resin printers are required for resin materials.
5. Post-Processing Considerations
Depending on the content, you may be willing to take on different amounts of post-print labor. Professional-looking finishes can be achieved by painting or smoothing materials like ABS and resin, if you’re willing to put in some post-processing time. Although PLA is simpler to work with, it might not be as smooth as ABS, which can be professionally finished with acetone vapor. Resin prints need to be cleaned and allowed to cure.
6. Safety and Environmental Factors
Your material selection should be influenced by the intended use of the printed product in that environment. While PLA’s performance may deteriorate in extreme heat or direct sunlight, PETG and ABS are more resistant to environmental factors including temperature and chemicals. Additionally, While PLA and PETG are less harmful and can be used in less ventilated locations, materials like ABS generate fumes and need to be ventilated.
By considering these factors, you can narrow down the material options to find the one that best suits your project’s needs, ensuring a successful print that meets your expectations.
Tips for Successful 3D Printing with Different Materials:
Achieving success in 3D printing with your chosen material hinges on understanding its properties and how to best work with it. Here are concise tips for printing with common materials:
PLA
Set the bed temperature between room temperature and 60°C, and start printing at a lower temperature of about 190–220°C. It is advised to print at moderate speeds since too rapid of a speed will affect layer adhesion. A cooling fan can hasten the solidification process and improve the sharpness of the details.
ABS
To reduce warping, use higher nozzle temperatures of 220-250°C and a heated bed of 80-110°C. It is recommended to print in a location with good ventilation and using an enclosure can assist by keeping the temperature constant. First-layer adhesion can be enhanced by using adhesives on the print bed, such as hairspray or a glue stick.
Resin
Before printing, make sure the resin is well combined and the build plate is precisely level. To prevent problems with detail and strength, modify the curing time for each layer according to the particular resin and printer model. To achieve the best polish and longevity, clean the prints with isopropyl alcohol and cure them with a UV lamp.
PETG
Print with the bed heated to 60–80°C, at a temperature that is somewhat higher than PLA (230–250°C). Slower print speeds can assist in preventing warping and blobs, and also improve layer adhesion, and reduce stringing.
By tailoring your approach to the specific requirements of each material, you can significantly improve the quality of your prints and reduce the likelihood of printing issues.
Post-Processing Steps for 3D Printed Miniatures:
Post-processing of 3D-printed miniatures involves several steps to enhance their appearance, strength, and functionality. These steps can vary depending on the printing technology used (e.g., FDM, SLA, SLS) and the material properties, but here is a general overview of the most common post-processing techniques:
1. Cleaning
Immediately after the print is complete, miniatures need to be cleaned to get rid of any excess material or residue as a result of the printing process. Depending on the type of print, the cleaning process for the miniature will look very different:
|
Type of 3D Print |
How to Clean Post Printing |
|
Resin-based prints (SLA/DLP) |
Clean the print in a bath of isopropyl alcohol (IPA) or a specialized cleaning solution to remove any uncured resin. This usually involves submerging the print and gently agitating it, followed by a rinse and sometimes a post-cure under UV light. |
|
Powder-based prints (SLS, MJF) |
Remove excess powder by brushing it off or using compressed air. This powder can often be reused for future prints. |
|
FDM prints |
Removed excess strings of filament or small blobs on the print with a pair of tweezers or a knife. |
2. Removing Supports
Many 3D printing processes require support structures that must be carefully removed after printing. This can be done using tools like pliers, cutters, or by hand if the supports are designed to be easily breakable.
3. Sanding and Smoothing
Sand the miniature to remove layer lines, support marks, and other imperfections. Start with coarse-grit sandpaper and gradually move to finer grits for a smooth finish. For resin prints specifically, chemical smoothing with a solvent or a specialized product can be used to achieve a glass-like surface finish.
4. Priming
Apply a primer coat to make the surface smoother and more uniform, which is especially important if you plan to paint the miniature. Priming also helps to reveal any remaining flaws that might need further sanding.
5. Painting
Painting adds color and life to your miniatures. Acrylic paints are commonly used for this purpose. It’s advisable to start with a base coat, followed by layers of detail, and finally, varnish to protect the paint job.
6. Gluing and Assembly
Some miniatures come in parts that need to be assembled after printing. Use a suitable adhesive (often super glue for plastics) to assemble your pieces accurately.
7. Curing
For resin-based prints, further curing under UV light might be necessary after cleaning to ensure the material reaches its final properties and strength.
8. Sealing
Finally, applying a sealant can protect the painted surface from handling and environmental factors. Matte or gloss varnishes can be used depending on the desired finish.
Safety Precautions When 3D Printing Miniatures
Maintaining safety during 3D printing and ensuring the longevity of your 3D printer, materials, and printed miniatures involves several important considerations. Here’s a comprehensive overview of key safety and maintenance tips:
- Ventilation: Some 3D printing processes, especially those involving the heating of materials, can release fumes that may be harmful if inhaled in large quantities. Ensure your printing area is well-ventilated, particularly when using ABS filament or resin printers.
- Handling Materials: Wear gloves when handling materials like uncured resin, chemicals used in post-processing, or hot components. Resin can be particularly irritating to the skin, and post-processing chemicals can be hazardous.
- UV Exposure: For resin-based printers, be cautious of UV light exposure to your skin and eyes. Use protective gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, when dealing with UV-curing processes.
- Fire Safety: 3D printers should be monitored, especially during long prints. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and ensure your printer is placed away from flammable materials. Consider using smoke detectors and automatic fire suppression devices designed for electronic equipment.
- Electrical Safety: Ensure your 3D printer is properly grounded, and avoid overloading electrical circuits. Regularly inspect cables and connectors for damage.
Maintaining Your 3D Printer for Optimal Performance
As they are the crux of any miniature creation, it is vital to ensure that the 3D printer itself is looked after carefully and good to go. There are several tips one can consider when maintaining their printer:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the printer and its components clean. Dust and filament debris can accumulate and affect print quality or even damage the printer. Pay special attention to the build plate, extruder nozzle, and any moving parts.
- Lubrication: Moving parts like rods and bearings should be lubricated periodically with appropriate oils or greases to ensure smooth operation and reduce wear.
- Firmware Updates: Keep your printer’s firmware up to date. Manufacturers often release updates that improve performance or add new features.
- Nozzle Care: Clean or replace clogged nozzles to avoid bad prints and potential damage. For printers that use filament, it’s also wise to check for filament quality and proper storage to prevent moisture absorption.
Maintenance Tips for Printing Materials and Miniatures
After printing, there is still much to do in terms of maintenance for miniatures and the materials needed to print them. Here are some things to take note of when it comes to the upkeep of materials and miniatures:
- Material Storage: Store filaments and resins in a cool, dry place to prevent them from degrading. Many materials absorb moisture from the air, which can significantly affect printing quality and the strength of the final print.
- Handling Miniatures: Printed miniatures, especially those made from certain resins, can be brittle. Handle them with care to avoid breakage. Use protective cases or display cabinets to protect them from dust and UV light, which can cause colors to fade or materials to degrade over time.
- Cleaning Miniatures: Clean your miniatures gently to avoid damage. For painted miniatures, use a soft, dry brush to remove dust. If needed, lightly dampen a cloth with water or an appropriate cleaner that won’t damage the paint or material.
Following these safety and maintenance guidelines will help ensure a safe printing environment, prolong the life of your 3D printer and materials, and keep your printed miniatures looking their best.
Learning Resources for 3D Printing Miniatures:
To dive deeper into the world of miniature 3D printing, several resources across the web cater specifically to learning about and discussing this niche. Whether you’re a beginner looking for tutorials or an experienced printer seeking advanced tips, here are some places where you can learn more about miniature 3D printing:
Recommended Websites and Blogs
There are several websites and blogs dedicated to 3D printing, each with an abundance of resources for miniature printers of any level to use. Here are a few examples of the most prominent ones:
- All3DP: Offers a variety of articles, guides, and tutorials on 3D printing, including sections dedicated to miniature printing for hobbies like tabletop gaming and model making.
- MyMiniFactory: While primarily a platform for downloading 3D printable files, MyMiniFactory also features blogs and tutorials focused on miniature printing.
- Instructables: Offers DIY guides and tutorials on a wide range of topics, including 3D printing. It’s a great place to find step-by-step instructions on creating 3D-printed miniatures and using 3D printers effectively.
YouTube Channels
In the age of the internet, people of the internet can virtually learn any hobby through the power of YouTube, and 3D miniature printing is no exception. Channels like 3D Printing Nerd, Tomb of 3D Printed Horrors, 3D Printed Tabletop, and Makers Muse specialize in reviews and tutorials for 3D printing miniatures, including tips on settings, materials, and painting. Even channels that do not solely focus on 3D printing, like Tabletop Minions, have videos with content relating to the topic that users can glean information from as well.
Online Courses and Tutorials
Nowadays, several websites and companies provide accessible online courses and tutorials on a variety of topics for anyone to learn at any time. The following are some websites that provide courses online for miniature printing.
- Udemy: Offers courses on 3D printing that occasionally include sections on miniatures or can be applied to miniature printing.
- Skillshare: Similar to Udemy, Skillshare features courses on 3D modeling and printing that can be useful for designing and printing miniatures.
Books
While more general, books on 3D printing can provide a solid foundation. Titles such as “The 3D Printing Handbook” by 3D Hubs or “Beginner’s Guide to 3D Printing” by Chuck Hellebuyck can be very helpful.
Manufacturer Resources
Many 3D printer manufacturers offer guides, tutorials, and community forums. If you own a printer, check out the resources provided by the manufacturer, as these can be tailored to your specific model.
Where to Find a Community for 3D Printing Miniatures:
Engaging with the 3D miniature printing community online can provide valuable insights, support, and inspiration for both beginners and experienced enthusiasts. Here are several platforms and forums where you can learn more about 3D miniature printing and connect with others in the field:
Forums
Forums are the most popular ways for members of the 3D printing community to interact. While many do access these forums on Reddit, there are also a variety of other websites that provide forums about miniature printing:
- Thingiverse: While primarily a repository for 3D printing models, Thingiverse also has a community section where users can discuss various topics related to 3D printing, including miniatures.
- PrusaPrinters Forum: A community forum hosted by Prusa Research, open to all 3D printing enthusiasts, not just Prusa printer owners. It’s a great place for discussions on printing techniques, troubleshooting, and model sharing.
- Ultimaker Community: Another printer manufacturer’s forum that welcomes all 3D printing enthusiasts. It’s particularly useful for professional and industrial users.
- 3DPrintBoard.com: A forum dedicated to all things 3D printing, with sections for different types of 3D printing technologies, materials, and showcases of completed projects.
Subreddits
Reddit is one of the biggest websites that allow users to come together and share insights. There are several subreddits dedicated to 3D printing that are great for advice, sharing projects, and finding resources:
- r/3Dprinting: A general 3D printing subreddit that covers a wide range of topics related to 3D printing technology, including miniature printing.
- r/PrintedMinis: Specifically focused on 3D-printed miniatures, this subreddit is an excellent place for sharing projects, tips, and techniques related to miniature printing.
- r/functionalprint: Focuses on practical, functional objects that members have printed, showcasing the utility aspect of 3D printing.
- r/minipainting: Dedicated to the art and craft of 3D printing miniatures for gaming, display, and other purposes.
Facebook Groups
Social media is another rising platform for communities of 3D printing aficionados to band together and share their insights. In particular, there are a variety of Facebook groups that 3D miniature printers join to learn and talk amongst each other:
- 3D Printing: A general group for 3D printing enthusiasts of all levels, sharing everything from basic questions to advanced project showcases.
- 3D Printing Geeks: Another active community focused on 3D printing technology, troubleshooting, and the latest industry news.
- Elegoo Mars/Mars Pro & Photon/Photon S: These groups are specific to owners and fans of particular resin printers, but there are many similar groups for different printer models.
Twitter and Instagram
These two platforms offer a great platform for visual inspiration for upcoming miniature printers. Follow hashtags like #3Dprinting, #3Dprinter, and #3Dprinted for posts from individuals and companies in the 3D printing sphere and examine their projects, innovations, and insights.
By following groups dedicated to 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing, professional networking sites like LinkedIn host several groups where professionals discuss industry trends, and job opportunities, and share insights into the future of 3D printing.
Sources for Downloading 3D Miniature Files
There are several websites where you can find a wide variety of files, ranging from tabletop game pieces to intricate display models. These websites often offer both free and paid files, catering to a broad spectrum of interests and skill levels. Here are some of the most popular websites for finding 3D printable miniature files:
1. Thingiverse
Thingiverse is one of the Internet’s most reliable and vast websites for 3D printing files (Credit: Thingiverse)
Thingiverse is one of the oldest and most popular websites for finding free 3D printable models. Created by MakerBot Industries, it caters to a wide range of interests, including art, fashion, gadgets, and particularly a large collection of components for DIY projects and educational tools.
It is also highly community-driven, with users often engaging in discussions, sharing modifications of existing designs, and collaborating on projects. Thingiverse is particularly popular among hobbyists and educators looking for accessible and diverse 3D printing options.
MyMiniFactory has some of the most unique and colorful miniatures models for download online (Credit: MyMiniFactory)
MyMiniFactory is a platform dedicated to 3D printable objects that are curated to ensure printability. Launched in 2013, it distinguishes itself by testing all uploaded designs for 3D printability, offering a mix of free and paid models. MyMiniFactory emphasizes quality and printability in its curated selection of 3D models, with a strong focus on miniatures for tabletop gaming, dioramas, and figures.
MyMiniFactory is known for its exclusive collections from renowned designers, making it a preferred choice for those seeking unique and high-quality miniatures. The platform also encourages interaction between designers and users, fostering a supportive community around 3D-printed miniatures.
3. Cults3D
Cults3D has designs for everything you might need for 3D printing, miniatures included (Credit: Cults3D)
Cults3D is a marketplace that connects 3D designers and users looking for 3D printing models. The site offers both free and paid 3D models across a variety of categories, including a robust selection of miniatures for gaming, collecting, and display. The platform supports independent designers by allowing them to sell their work, which means users have access to a wide range of unique and professionally designed miniatures.
Shapeways is a platform that takes miniature printing to a whole new level business-wise (Credit: Shapeways)
Shapeways is a global 3D printing service and marketplace where users can design, buy, and sell their 3D-printed products. Shapeways differs from the other platforms as it provides a print-on-demand service, allowing designers to sell their miniatures directly to consumers without needing to own a 3D printer.
CGTrader provides a variety of downloadable 3D files for miniatures of every occasion (Credit: CGTrader)
CGTrader is one of the largest marketplaces for 3D models, catering not just to 3D printing but also to virtual and augmented reality, and gaming applications. It has a significant selection of 3D printable miniatures, including characters, creatures, vehicles, and terrain. CGTrader attracts professional 3D artists and designers, offering both free and paid models.
Key Takeaways from the 3D Printing Miniatures Guide
Learning and mastering the process behind printing 3D miniatures can be one that is tedious and time-consuming, and may take many instances of trial and error to get it right. However, once mastered, miniature printing can be an extremely rewarding skill.
We encourage you to experiment continuously! Try different materials, techniques, and printing files. As they say, practice makes perfect. If you want to learn more about 3D printing, check out this guide regarding 3D printing miniatures or you can visit R3DMAKERS’ official website for additional 3D printing tips.








