The Comprehensive Guide to 3D Print Carbon Fiber

Discover the cutting-edge world of 3D printing with the unmatched strength and durability of carbon fiber. With its exceptional mechanical properties, lightweight nature, and robustness, carbon fiber has become the go-to material for various high-performance engineering applications, auto body prototypes, factory tools, and more. While carbon fiber has been popular since the 1960s, its integration into 3D printing has recently taken center stage, providing plastic parts with metal-grade strength and resistance to heat, chemicals, and corrosion. At All3DP, we delve deep into the realm of 3D print carbon fiber, engaging with material manufacturers, 3D printer creators, service providers, and industry professionals to bring you the latest insights on this groundbreaking technology. Join us as we explore why engineers, machinists, and makers alike are embracing 3D print carbon fiber for their most demanding projects.
What Is Carbon Fiber 3D Printing?

3D printing carbon fiber is a skill that involves incorporating chopped or continuous carbon fiber material into a polymer powder or filament. This fusion of carbon fiber with a polymer base, such as Nylon or PEEK, gives rise to a category of 3D printing often referred to as “composite” 3D printing. The proportion of carbon fiber in the material can vary depending on the desired properties.
ADVANTAGES:
- Strong and Lightweight: Carbon fiber’s impressive strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for performance products due to its low density.
- Heat Resistance: Carbon fiber can withstand higher temperatures than many polymers and can even enhance the High Deflection Temperature (HDT) of composite materials.
- Stiffness: Carbon fiber maintains its shape under high stress, providing excellent stiffness without sacrificing strength or durability.
DISADVANTAGES:
- Expensive: Carbon fiber’s complex manufacturing processes result in higher costs, making it a luxury material found in high-end products rather than mass-market items.
- Brittle: Despite its stiffness, carbon fiber can be brittle and susceptible to shattering under high impact force, limiting its suitability for certain applications.
Two primary 3D printing technologies utilized for carbon fiber printing
Carbon Fiber FDM:

- Versatile method for creating carbon fiber parts.
- Use hardened steel nozzle with carbon fiber filament.
- Provides strength and stiffness to prints.
Carbon Fiber SLS
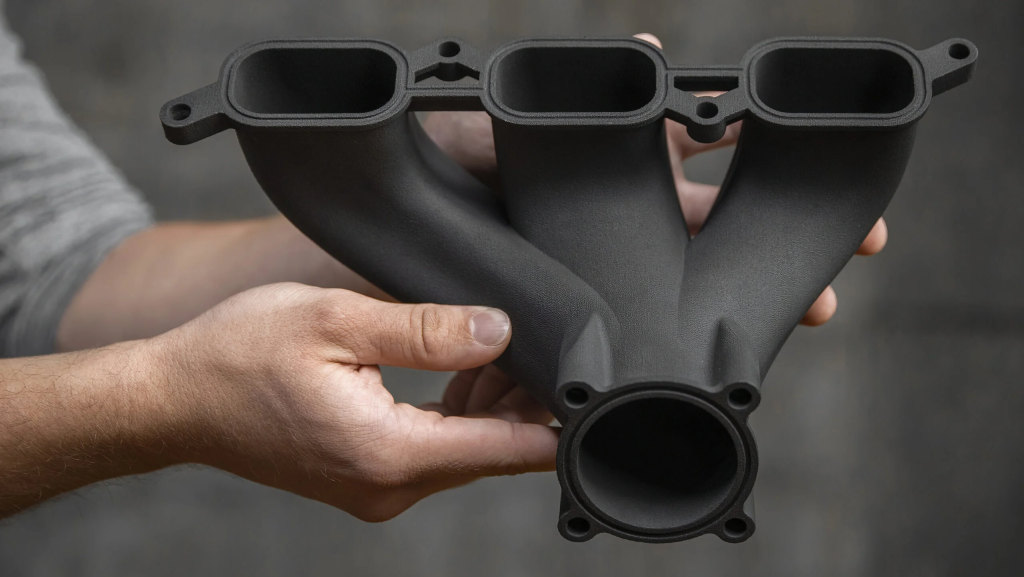

- Utilizes high-powered lasers and powdered plastic.
- Produces finely detailed, strong, and heat-resistant parts.
- Carbon fiber-filled nylon is a popular material.
- Anisotropic properties require careful part orientation.
- New affordable benchtop machines with proprietary powders available.
The top benefits of carbon fiber 3D printing are:
1. High strength and stiffness.
2. Ideal substitute for metal in various applications.
3. Exceptional dimensional stability.
4. Suitable for both end-use parts and functional prototypes.
5. Resistant to corrosion, heat, oil, and grease.
6. Reduced weight while maintaining strength, making it valuable in automotive, aerospace, and sports industries.
What Are the Best Carbon Fiber 3D Printers?
Consider these aspects when choosing a printing carbon fiber 3D printer:
- Cost of printer and materials
- Mechanical properties needed
- Level of detail required
- Print size and speed
- Material options (open vs. proprietary)
- Specific market needs (automotive, aerospace, manufacturing)
For small to medium-sized projects, explore desktop-size models ($4,750 – $75,000) with infused and continuous carbon fiber FDM. Industrial-level options ($15,000 – $250,000+) are available for larger-scale production.
At All3DP, we reviewed the Markforged Mark Two, impressed by its flawless prints and easy-to-remove supports. Design parts to minimize support usage for best results.
When selecting carbon fiber filament, consider the following factors:
- Infused polymer (PLA, PEEK, PETG, etc.)
- Percentage of carbon fiber strands (% by weight)
PLA with carbon fibers offers improved strength, though not as strong as metal. Nylon or PEEK combined with carbon fiber provides significant reinforcement.
Higher percentage of carbon fiber generally means better reinforcement, with 20% being a common amount.
For beginners, there’s no need to search extensively for the best carbon fiber filament. Check out our guide below.
In industrial 3D printed carbon fiber, specific brands may restrict filament options. Continuous carbon fiber materials necessitate specialized machines with hardware to incorporate the continuous strand into the base material.
THE COST OF 3D CARBON FIBER 3D PRINTER
Carbon fiber filament
- The cost of carbon fiber filament varies depending on several factors.
- On the lower end, a 1-kilogram spool of CFF filament can cost around $50, comparable to standard filaments for desktop FDM printers.
- However, prices can significantly increase for specialized filaments, such as Markforged’s Onyx, with an 800-gram spool retailing at $230.
- Prices can further escalate when specialized printers are required for carbon fiber 3D printing.
- It’s crucial to understand the specific requirements of your parts to avoid excessive spending.
- Check our filaments guide for material-specific details on a variety of chopped carbon fiber filaments.
Carbon Fiber Polymer Powder
SLS powders tend to be pricier, exemplified by Formlabs PA 11 CF and Sinterit PA 11 CF, priced at around $1,000 per 6 kg unit. EOS’ HT-23 powder cost is undisclosed, indicating it may not be budget-friendly.
However, Recycling carbon fiber is challenging due to its toughness. Much of the waste is sent to landfills or incinerated. Ongoing research aims to reclaim and recycle carbon fiber printed products for sustainability. Consider using materials made from recycled carbon fibers and polymers for a more eco-friendly approach in 3D printing.
Is Carbon Fiber Harmful & Toxic?
- Carbon fiber 3D printing carries specific material-related risks in addition to standard 3D printing hazards.
- Handling carbon fiber-reinforced SLS powder can release airborne microscopic carbon fibers, leading to respiratory irritation and problems.
- Adequate workspace ventilation and personal protective equipment (masks, gloves) are essential to mitigate these risks.
- For infused and continuous carbon fibers, the risk of airborne fibers is minimized, but smoke and fumes from molten materials remain a concern.
- Carbon fibers are often combined with petroleum-based plastics (nylon, ABS, PETG), requiring proper ventilation and protective gear to avoid inhaling aerosols and VOCs.
Software for Carbon Fiber Print
- All 3D print carbon fiber require operating software to convert digital models into machine instructions.
- Filament 3D printers typically use standard slicing software for this purpose.
- Chopped fiber filament printing can be accomplished with the accompanying desktop machine’s software, as long as it meets the filament’s specifications.
- Advanced materials and technologies may require specialized slicing software due to material-specific parameters like carbon fiber reinforcement strategies.
- For instance, Markforged offers their proprietary cloud-based file preparation and management software, Eiger, with each printer.
- Eiger now includes virtual testing through simulation, allowing for smart carbon fiber reinforcement validation and optimization before printing with a simple click.

Where to order?
3D printing service providers offer affordable printing services and expert advice on materials and technologies suitable for your specific needs. They are a practical choice when the quantity of required parts doesn’t justify investing in a 3D printer or when you want to explore various options.
Craftcloud, powered by All3DP, is a marketplace that connects you with over 100 3D printing service providers worldwide. There’s no minimum 3D print carbon fiber order requirement, and the process is straightforward: upload your CAD model, choose your desired material and finish, and receive instant real-time quotes without hidden fees.
Craftcloud’s extensive library of materials includes carbon-fiber-infused filaments mixed with PETG, PLA, ABS, nylon, polycarbonate, and PEEK, as well as proprietary materials like Markforged Onyx and Extrudr GreenTEC Pro Carbon. They also offer CCF filaments in Nylon and PETG, along with carbon-fiber-reinforced nylon SLS powders, perfect for functional prototypes, jigs, and end-use parts.