PETG vs PLA: A Comprehensive Comparison of 3D Printing Filaments

In the ever-evolving world of 3D printing, the selection of the right material plays a crucial role in achieving the desired output. Among the various materials available for 3D printing, PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified) and PLA (Polylactic Acid) are two of the most popular choices. This article aims to provide a comparison of PETG vs PLA, considering factors such as strength, flexibility, and more. While PLA has long been admired for its biodegradable properties and ease of printing, PETG offers higher durability and impact resistance.
The choice between these two materials often depends on the specific requirements of a project, ranging from the desired appearance to the mechanical performance of the printed object. For those interested in more environmentally-friendly options, PLA might be the preferred choice, while those seeking a more robust and flexible material might opt for PETG. In the following sections, we will explore the properties of each material, delve into the comparisons of PLA+ vs PETG, and look at practical applications to help you determine the best choice for your 3D printing needs.
Introduction: Understanding PETG and PLA Filaments
Before diving into the comparison of PETG filament vs PLA, let’s understand the basics of these two materials. PLA, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch, is known for its biodegradability and is often used for decorative items and models. On the other hand, PETG is a variation of common PET plastic that offers higher flexibility and strength, making it suitable for functional parts and prototypes. Both materials have distinct characteristics and applications, providing various options for 3D printing enthusiasts.
PLA (Polylactic Acid) Overview
PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources like cornstarch or sugarcane. It’s known for its ease of printing, making it a popular choice for beginners.
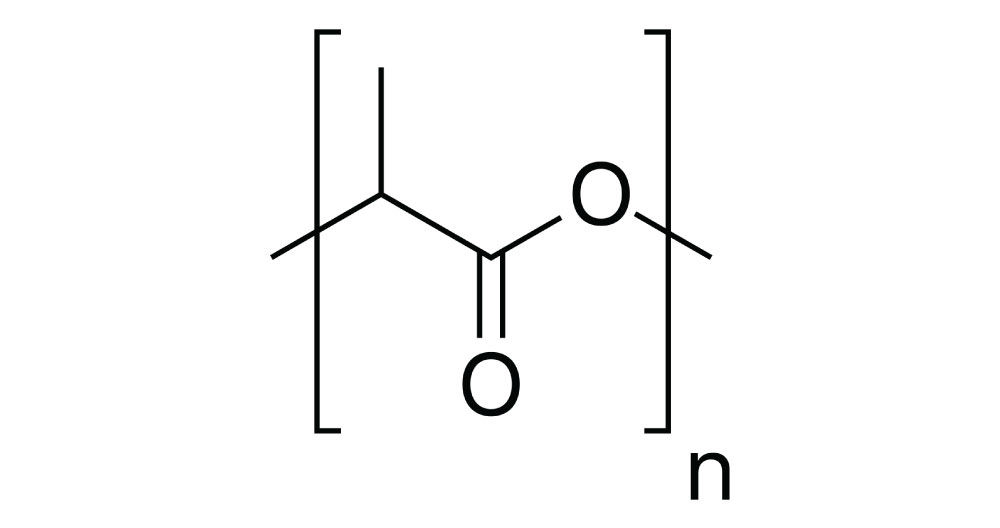
Reference : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polylactic_acid
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified) Overview
PETG is a variation of the commonly used PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) plastic. It offers greater flexibility and strength and is favored in applications that require durability.
Reference : https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/13/12/2673
Key Differences Between PETG and PLA
1. Strength and Durability
Is PETG Stronger than PLA?
Yes, PETG is generally stronger and more flexible than PLA. It has higher impact resistance, making it suitable for functional parts and prototypes.
PLA+ vs PETG
PLA+ is an improved version of PLA with enhanced strength, but even then, PETG often surpasses it in terms of durability.
2. Printing Temperature
PETG: Requires higher printing temperatures (230-250°C).
PLA: Prints at a lower temperature range (180-220°C).
3. Print Speed and Ease of Use
Printing with PLA vs PETG: PETG can be trickier to print with, requiring more precise control and calibration.
PLA: Known for its ease of printing, making it suitable for beginners.
4. Environmental Impact
PLA: Biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, PLA is considered more eco-friendly.
PETG: Though recyclable, PETG’s production and disposal are more taxing on the environment.
5. Aesthetics and Finish
PETG: Offers a glossy finish and is more transparent.
PLA: Provides more color options and generally exhibits a matte appearance.
6. Chemical Resistance
PETG: Known for its higher chemical resistance compared to PLA.
PLA: May degrade when exposed to certain chemicals.
7. Cost
PLA: Generally cheaper than PETG.
PETG: A bit more expensive but offers added benefits in strength and flexibility.
Applications: Where to Use PETG and PLA?
PLA: Ideal for decorative objects, models, and non-functional prototypes.
PETG: Suitable for mechanical parts, containers, and items that require durability.
Safety Tips for Using PETG and PLA
When printing with PETG vs PLA, it is crucial to consider safety aspects. PETG may release fumes during printing, requiring proper ventilation. PLA, on the other hand, is generally considered safer for indoor printing.
Reference : https://shop.anima.gr/petg-vs-pla-filament
Conclusion
The choice between PETG and PLA largely depends on the specific requirements of the project. Here’s a quick guide to choosing:
- For Strength and Durability: Choose PETG, especially if the question arises, “Is PETG stronger than PLA?”
- For Ease of Printing and Eco-Friendliness: Opt for PLA.
- For Improved Strength with PLA: Consider PLA+ vs PETG, though PETG may still offer better durability.
3D printing enthusiasts must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each material, considering factors like cost, appearance, strength, and environmental impact. While PETG offers higher strength and flexibility, PLA is beloved for its ease of use and environmental friendliness. Ultimately, the debate of PETG vs PLA doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all answer. The decision should align with the specific needs and goals of the project, whether it’s a hobbyist’s creative endeavor or a professional’s functional prototype.
Both materials have their unique places in the 3D printing world, and understanding their characteristics helps in making an informed choice. It’s important to recognize that advancements in technology and manufacturing processes continue to bring new variations and improvements to both PLA and PETG, expanding their applications and features. Many professionals conduct trial prints with both materials to evaluate their performance under specific conditions, a practice that can help in making a more precise selection. By thoroughly considering the factors such as “is PETG stronger than PLA?”, “printing with PETG vs PLA“, and evaluating cost implications, users can align their choices with their objectives and optimize the overall 3D printing process for successful outcomes.