The Future of Agriculture with 3D Print Farming
The agricultural sector, traditionally rooted in age old practices, is now venturing into the realm of modern technology. One of the standout technological integrations is the utilization of 3D printing in agriculture. This 3D print farming is revolutionizing the way we cultivate, manage, and envision our farmlands.
With a global emphasis on sustainability and food security, integrating advanced technologies into farming has become more than a luxury — it’s a necessity. 3D print farming can significantly reduce waste, leading to more eco-friendly farming practices. Furthermore, it promotes a seamless bridge between digital advancements and physical cultivation, enhancing the entire agricultural supply chain.

How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing Agriculture
Agriculture has always been the backbone of society, continuously adapting to cater to growing populations and ever-changing needs. With the fusion of 3D printing in agriculture, we are embarking on an era where efficiency, customization, and innovation hold the reins. Farmers are continually searching for ways to maximize their yields and optimize their operations. Here, the versatility of 3D printing agriculture comes into play.
By turning digital designs into physical objects, farmers can tailor their tools and equipment to specific tasks, creating a more streamlined approach to farming. This integration is also driving down costs, allowing farmers to innovate without substantial financial constraints. Additionally, it opens doors for young tech-savvy individuals to consider farming as a viable and modern career path.
Key Uses of 3D Printing in Farming
Tailored Tools and Equipment
One of the most exciting benefits of 3D printing in agriculture is the production of custom tools. From specialized plows tailored for specific soil types to irrigation systems designed for unique terrains, 3D printed farm equipment provides farmers with tools that cater precisely to their needs. No more one-size-fits-all; farming equipment can now be as unique as the crops they help cultivate. Such bespoke tools can lead to more effective farming techniques, thus potentially increasing yields. With reduced equipment malfunctions due to tailored designs, farmers can expect a smoother operational flow.

Quick Spare Parts Manufacturing
Farm machinery is often susceptible to wear and tear. Previously, replacing broken parts meant waiting for shipments or searching for compatible components. Now, with a 3D printer farm on-site, farmers can quickly print the necessary parts, reducing downtime and maintaining a steady workflow. This on-the-spot manufacturing capability reduces the reliance on external suppliers, ensuring that farming operations remain uninterrupted. Moreover, the flexibility of 3D printing means that parts can be improved upon or modified with each print, leading to better machinery performance over time.
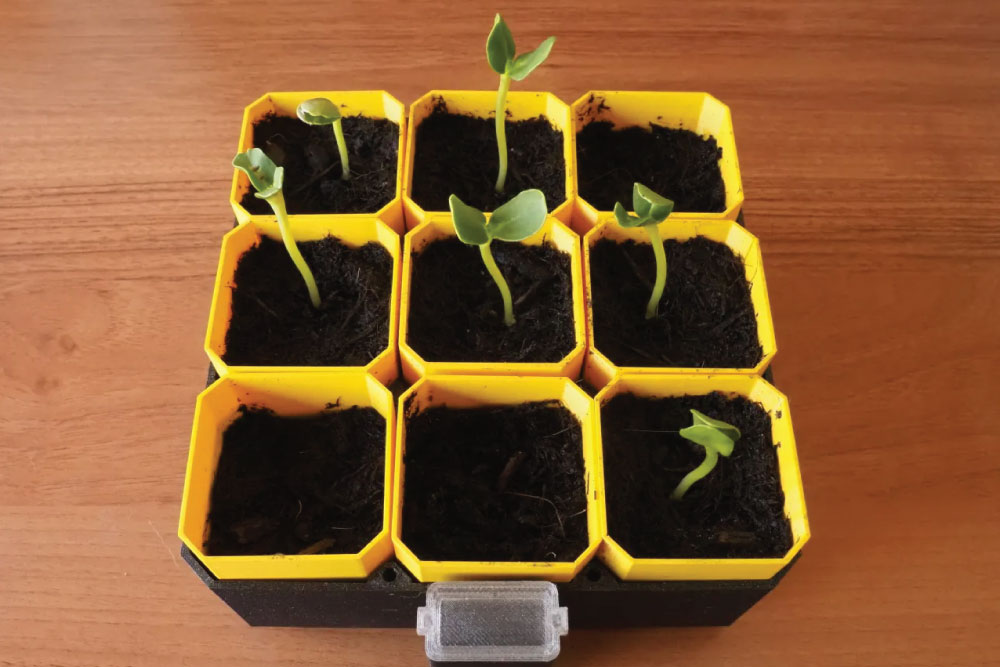
Accurate Seeding
3D print farming has introduced advanced tools that aid in precise seeding, ensuring optimal space between seeds, which can lead to better crop yields. These tools are not just efficient but can also be customized for different seed types, making the seeding process more streamlined. Enhanced accuracy means that seeds have a higher likelihood of germinating and growing into healthy plants. This precision eliminates the overuse of seeds, saving both resources and costs. In the long run, consistent use of such tools can lead to significant enhancements in overall crop quality.
Creative Farm Structures
From optimized greenhouse designs to intricate trellis structures, 3D printing allows for the creation of unique and efficient farming structures. Such innovations can lead to enhanced plant growth and better protection from pests or harsh environmental conditions. These structures can be tailored to specific geographic locations and climates, ensuring they meet the unique requirements of each farm. Rapid prototyping via 3D printing also allows for continual improvements and modifications to these structures. As farming environments change due to factors like climate change, these adaptable structures can evolve in response.
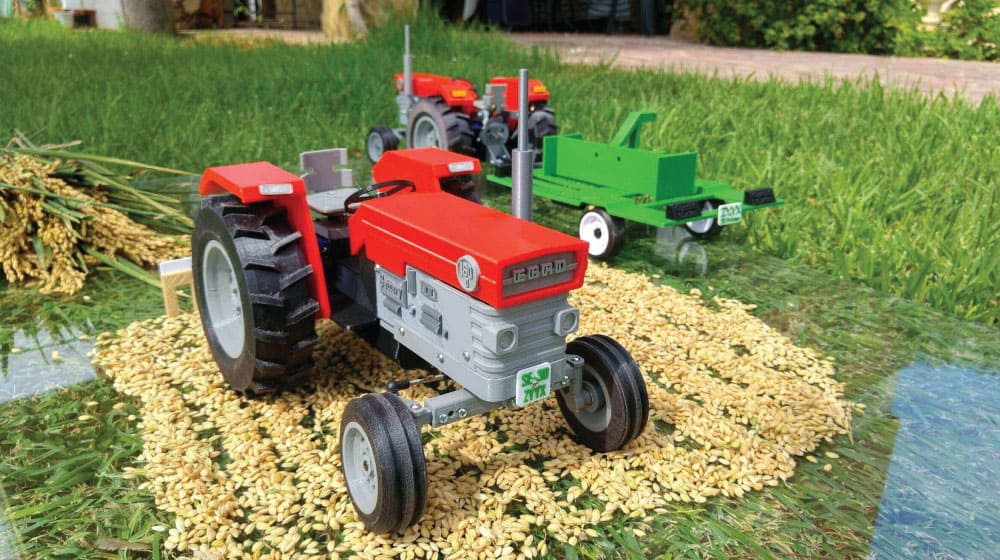

Training with Educational Models
3D printer farms can produce detailed models of crops, soil layers, and farming techniques. These models serve as excellent educational tools, helping train the next generation of farmers by offering a tangible, hands-on approach to learning. Furthermore, these models can be a boon for agricultural researchers, allowing them to visualize complex processes and phenomena. With global agriculture facing numerous challenges, training and educating budding agriculturists becomes paramount. These 3D printed models can make abstract concepts tangible, fostering a deeper understanding.
Conclusion
3D print farming is not just a fleeting trend but a transformative force reshaping the agricultural landscape. By providing solutions that are efficient, customizable and innovative, 3D printing in agriculture is sowing the seeds for a future where farming is more sustainable, productive, and in tune with the environment. As the fields of technology and agriculture continue to intertwine, one thing is clear: the future of farming is three dimensional.
This integration represents the convergence of two seemingly distinct fields, leading to unexpected innovations. With challenges like climate change, food security and population growth, 3D print farming could be the key to sustainable solutions. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in agriculture, 3D printing stands out as a beacon of hope.







